What are you looking for?
20. June 2018
Cyber-physical systems and logistics
Cyber-physical systems, or CPS for short, are system units or components that are linked together by means of software, electronics and mechanics, the so-called cyber-physical infrastructure. The technologies from the 'Internet of Things' (IoT) and…
24. May 2018
Logistics management and the supply chain
The integrated planning, organization, management, processing and control of the entire flow of materials and goods and the corresponding information flow is called logistics management. This is not a tangible work step, but rather countless process…
16. May 2018
Vogel’s approximation method
The approximation method according to Vogel is a heuristic procedure that is mainly used in distribution logistics, for example to solve a transport problem. It belongs to the field of mathematically oriented statistics, also called operations…
19. April 2018
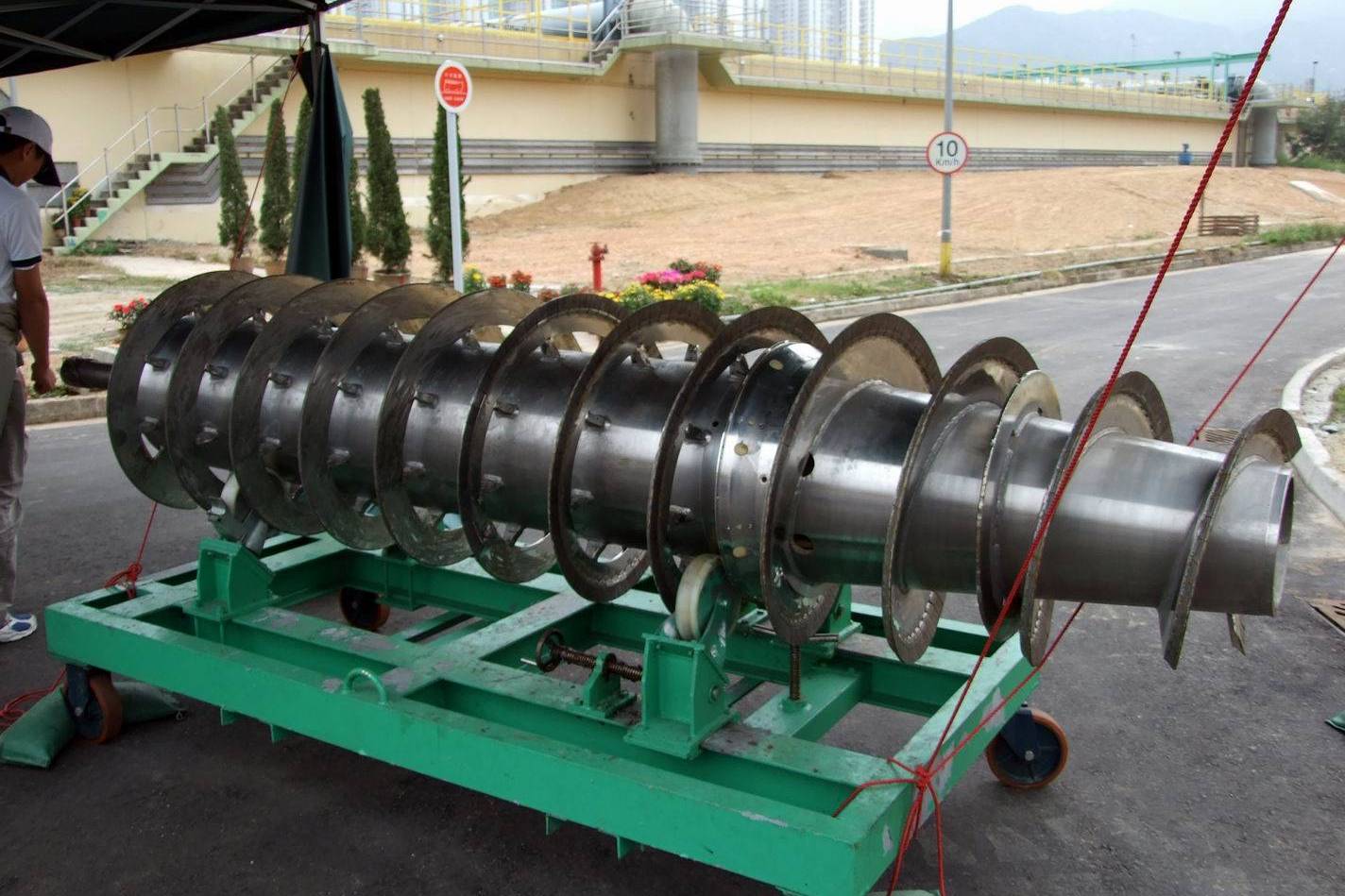
The screw conveyor / spiral conveyor for bulk material
Transport systems are needed in warehouses to transport goods. For this purpose, there are various possibilities for different requirements in conveyor technology. In addition to roller, vibratory and circular conveyors, screw conveyors (also known…
6. March 2018
Opportunity costs in logistics
Opportunity costs, also known as alternative costs or foregone costs, express a foregone benefit in costs on the basis of decisions that have a negative impact and enable an approximately accurate cost calculation. The degree of utilization always…
8. January 2018
CPFR – Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment
CPFR stands for Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment and is a further development of Efficient Consumer Response (ECR), known from supply chain management. CPFR requires that all information along the value chain is brought together…
5. December 2017
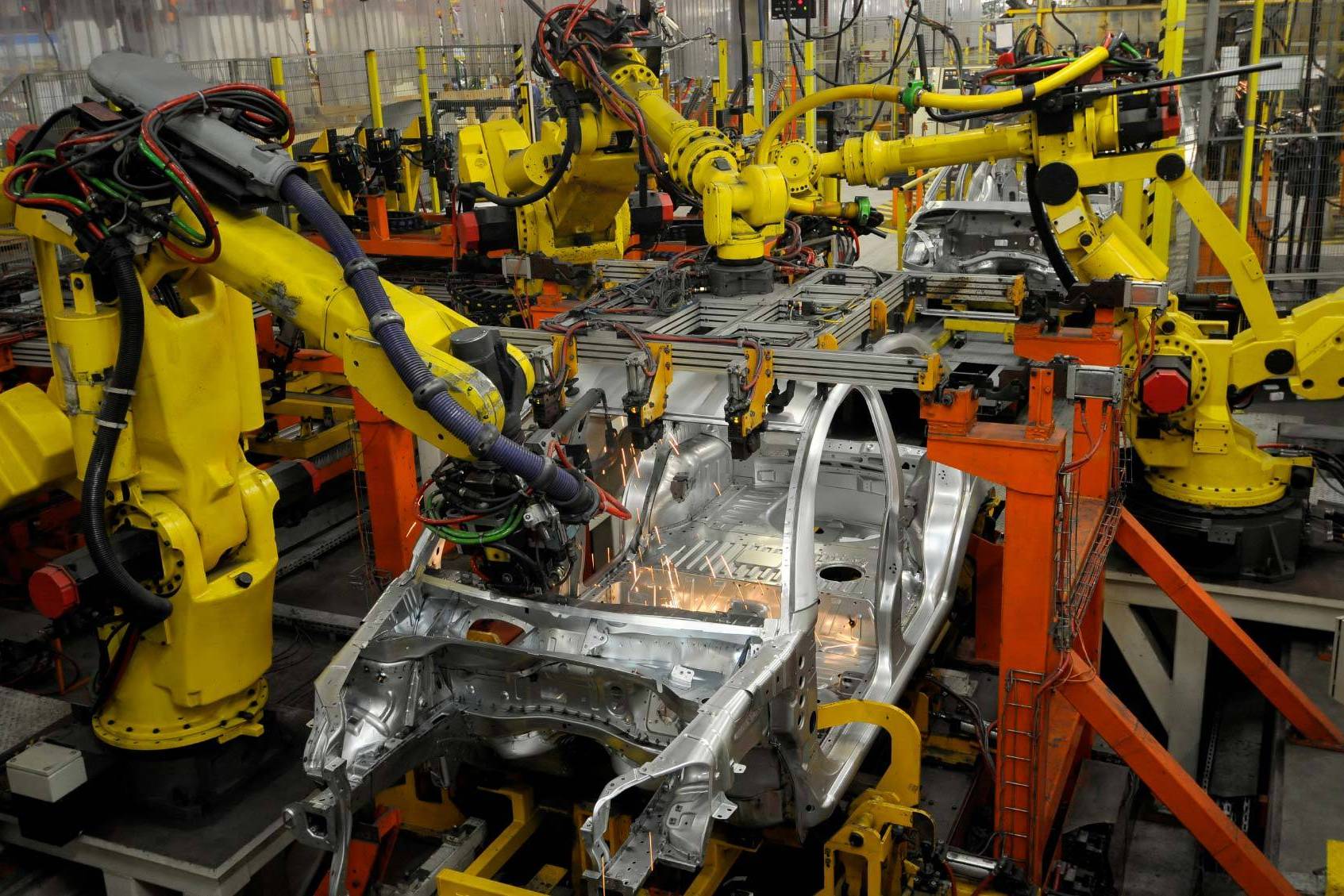
Networked Production: Computer-integrated Manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing, or CIM for short, stands for computer-controlled machine and automation systems, which are generally used in the manufacture of products. CIM uses different technologies and their technical functions such as…
28. November 2017
At a glance: the enterprise resource planning system
An enterprise resource planning system is a software that ensures a smooth flow of commercial processes within a company. The recording and optimization of inventory movements and stocks, scheduling, sales and purchasing can also be handled on a…
14. November 2017
The picking time in intralogistics
The picking process itself and the associated picking time are usually a conglomerate of personnel- and cost-intensive processes, whose complexity depends on the business processes of the company. The picking time is the time required to complete a…
24. October 2017
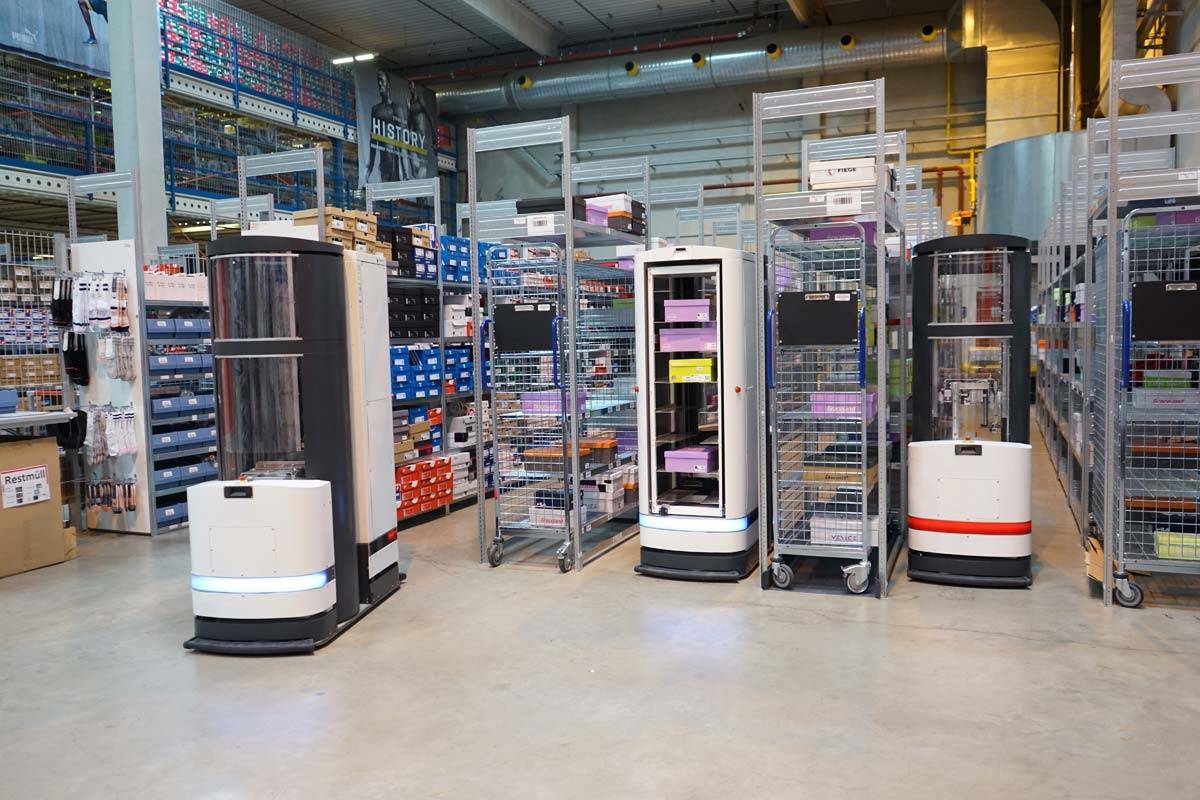
Picking method Pick-by-robot
The picking type Pick-by-Robot means the picking of goods, carried out by so-called perception-controlled logistics robots - without human intervention. Perception-controlled logistics robots are a further development of autonomous systems that…
16. October 2017
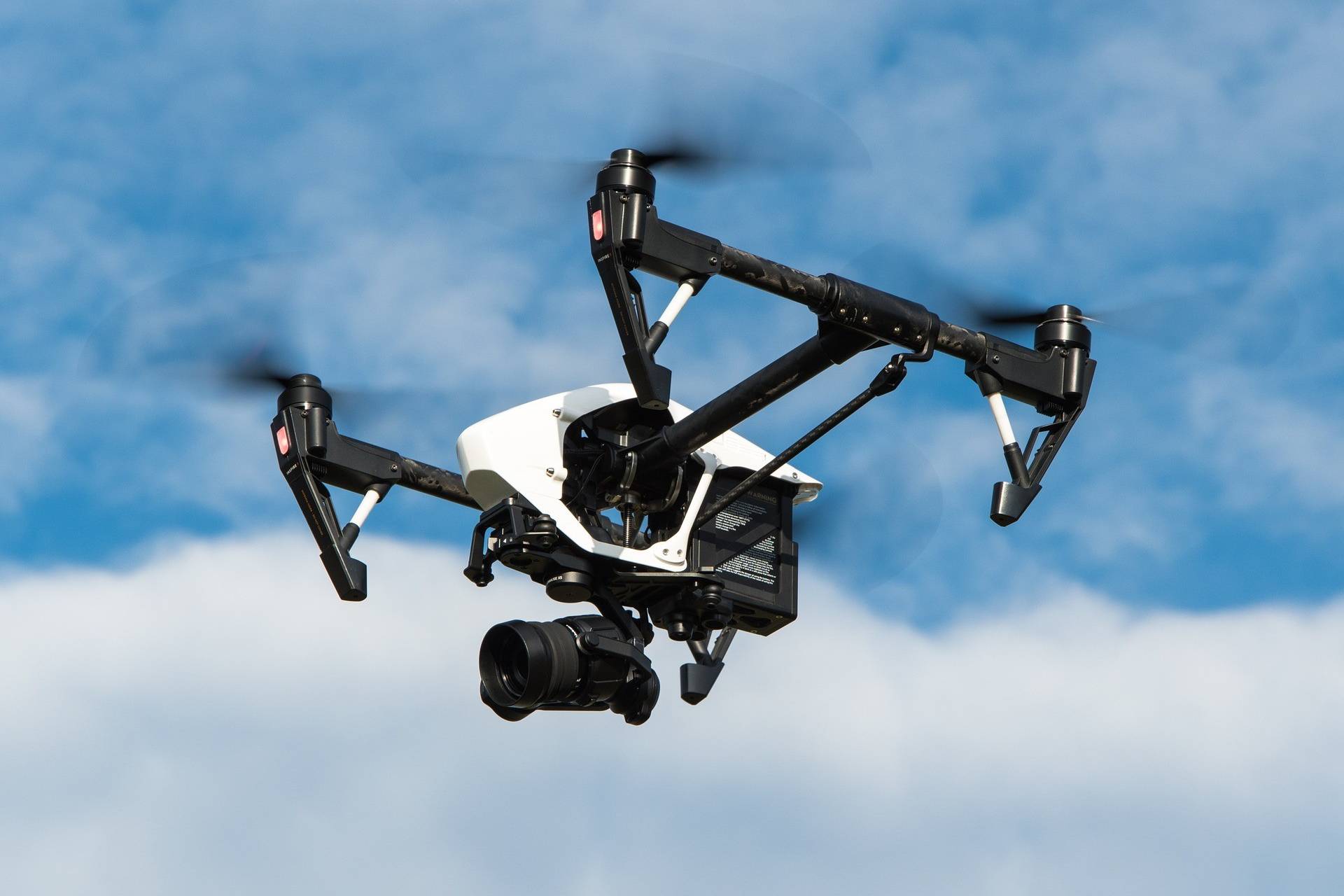
Multicopter: Drones as parcel carriers of the future
Goods delivery by automated or even autonomous drones? What we know at best as a vision from science fiction films could soon become everyday life. At least when it comes to Amazon, UPS, Mercedes Benz and DHL. What are the challenges, what is…
10. October 2017
Picking type Pick-by-Scan (also Pick-by-PDT)
The picking method Pick-by-Scan is a paperless picking process that is supported by a portable data collection terminal, PDT for short. The PDT replaces the classic picking list in paper form. Mobile handheld computers with integrated 1D or 2D…
25. September 2017
Human-machine interfaces in the industry
The human-machine interface represents the analog or digital interaction interface between a person, i.e. a user, and a machine. It is a part of human-machine communication (also human-machine interaction). In its simplest form, this interface can…
18. September 2017
Kanban and swarm intelligence at management level
In manufacturing and industry, a supply concept called Kanban(Japanese for card or sign), invented and developed by Taichi Ohno in the Toyota factories of the 1950s, has established itself worldwide. Like the swarm intelligence, the Kanban principle…
12. September 2017
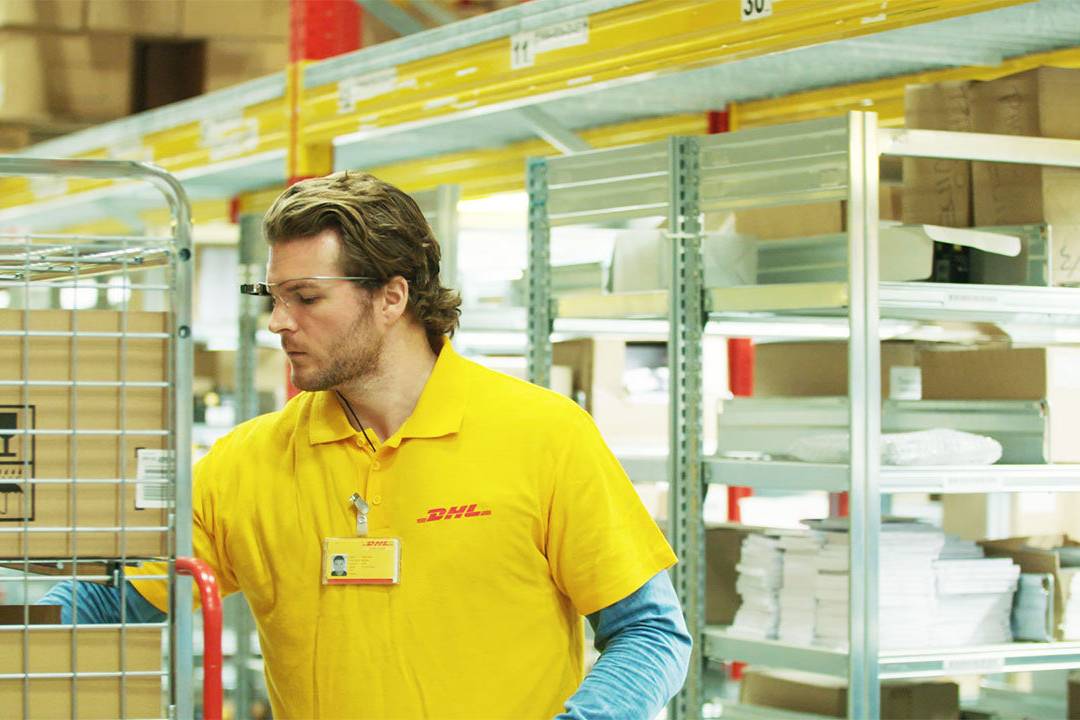
The picking method Pick-by-Vision
Pick-by-Vision is a picking process in which a picker uses data glasses and context-related information to compile articles or goods for customer or production orders. The data glasses, also known as smart glasses, not only continuously supply the…
1. August 2017
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
The term Product Lifecycle Management, PLM for short, describes a holistic approach to pooling product information. It is a kind of cross-company management and control of the information flow of a product along the entire value chain. The industry…
18. July 2017
The control center in intralogistics
The control panel in intralogistics represents a central point of a warehouse management system and supports the employees responsible in the entire warehouse operation control process. In addition to the consolidation of information (key figures),…
19. June 2017
Augmented Reality in logistics and service
Augmented Reality (AR) describes the computer-aided extension of human perception of reality. From the users point of view, the real and virtual worlds merge with each other. The advantage: Through the use of cameras, sensors and high-resolution…
29. May 2017
Exoskeletons in logistics and production
Exoskeletons, also known as outer skeletons or support robots, are support structures worn on the body, which reduce the load on the body and reduce the risk of injury by means of (electro-)mechanical support. Exoskeletons are still at an early…
23. May 2017
Smart Data
Smart Data stands for the detailed and structured result of an analysis of unstructured data masses (Big Data). Every smart data information is an explicit fact. These are also known as digital findings, which also allow links to other fine-grained…
12. May 2017
The Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Supply chain management (SCM) stands for the monitoring process as well as the coordination and control of the supply chain (value chain). This involves the allocation of all materials, information and the finances distributed along the supply chain…
8. May 2017
Logistics – Definition
The term logistics stands for the planning, control and monitoring of the material and immaterial flow of goods within a company, between partner companies and between suppliers and end customers.
18. April 2017
Key figure system in intralogistics
Although a complete bundling of all key figures arising in warehouse and distribution systems is possible nowadays, it is difficult due to the multi-layered nature of complex systems. Using a predefined key figure system, it is possible to compare…
18. April 2017
Effects of shipping options on loyalty to the online store
Buying on the Internet offers almost endless possibilities and shipping options. Whether books, clothes, food - regardless of the time of day, one can buy almost any imaginable product in countless stores. The providers are also becoming more and…
30. March 2017
Conveying aids in intralogistics
In intralogistics, conveying equipment is used to combine individual goods into larger load units. In general, the following definition applies: intralogistics uses conveying equipment to protect different goods, make them ready for loading,…
22. March 2017
Order picking times – Dead time
Dead time is an unproductive but unavoidable so-called auxiliary time, which arises during picking due to preparatory and follow-up activities (e.g. search and identification of the storage location). It can be optimized by simple measures.
9. March 2017
The (hanging) bag sorter
The Pouch sorter / Bag sorter belongs to the category of logistic sorting and distribution systems. A (hanging) bag sorter system makes it possible to transport hanging and flat packed goods fully automatically on the same line - even classic…
1. March 2017
Order picking – process steps
Picking stands for the combination of predefined orders from a warehouse assortment. The process steps that are carried out during picking include, for example, transferring the picking order and retrieving the article. These are individual basic…
23. February 2017
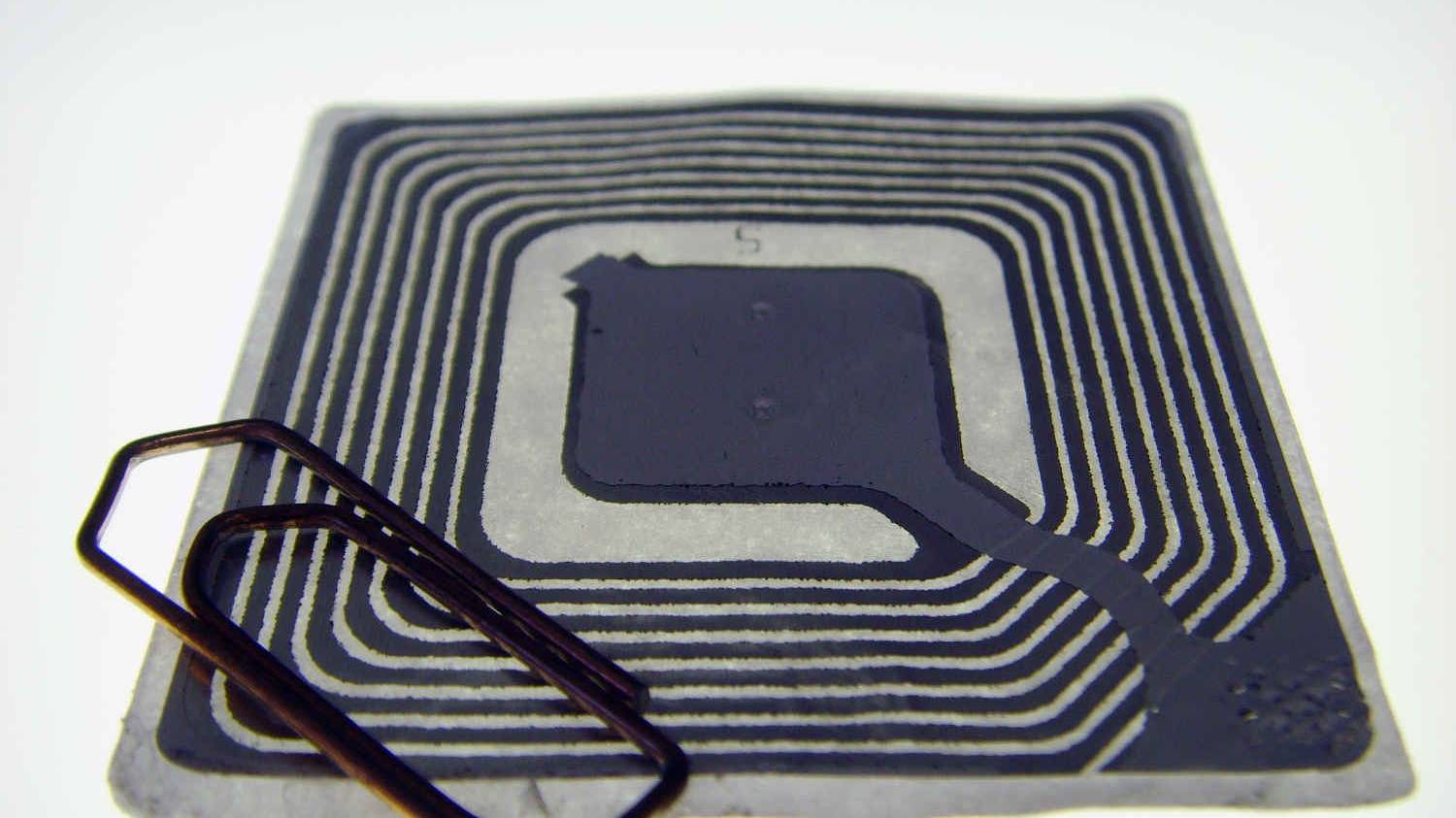
Advantages of RFID technology over barcodes
What advantages does RFID radio technology have over barcodes? This question has also been on the agenda of intralogistics for some time now. In principle, more information is available with the conventional use of RFID. Moreover, logistics and…
16. February 2017
The picking travel time
The order-picking way time is the sum of the time required for picking a single order or batch; measured from the starting point of picking via the picking locations to the delivery point - depending on the picking method, including the way back to…
6. December 2018
Out-of-Stock – the gap in the shelf
Out-of-stock typically refers to a shelf space in the stationary retail trade which no longer…
15. November 2018
The production cycle
In a broader sense, a production cycle is the production process that begins with the raw materials…
7. November 2018
Inventory in companies and in logistics
In the inventory, the assets of a company are determined on a key date; in this way, assets and…
16. October 2018
Insulated packaging: Maintaining the cold chain in the supply chain
Insulated packaging is used for products that are sensitive to temperature or environmental…
28. September 2018
Uses of Blockchain technology in logistics / intralogistics
Blockchain is an enabling technology. Just like the Internet, it harbors technological properties…
29. August 2018
Storage maintenance costs – warehousing costs or storage costs
Trading companies and manufacturing companies usually have a warehouse or distribution centre. Raw…
15. August 2018
The Jidoka principle in production and logistics
The Jidoka principle describes the ability of a machine, a plant or an entire system to switch…
31. July 2018
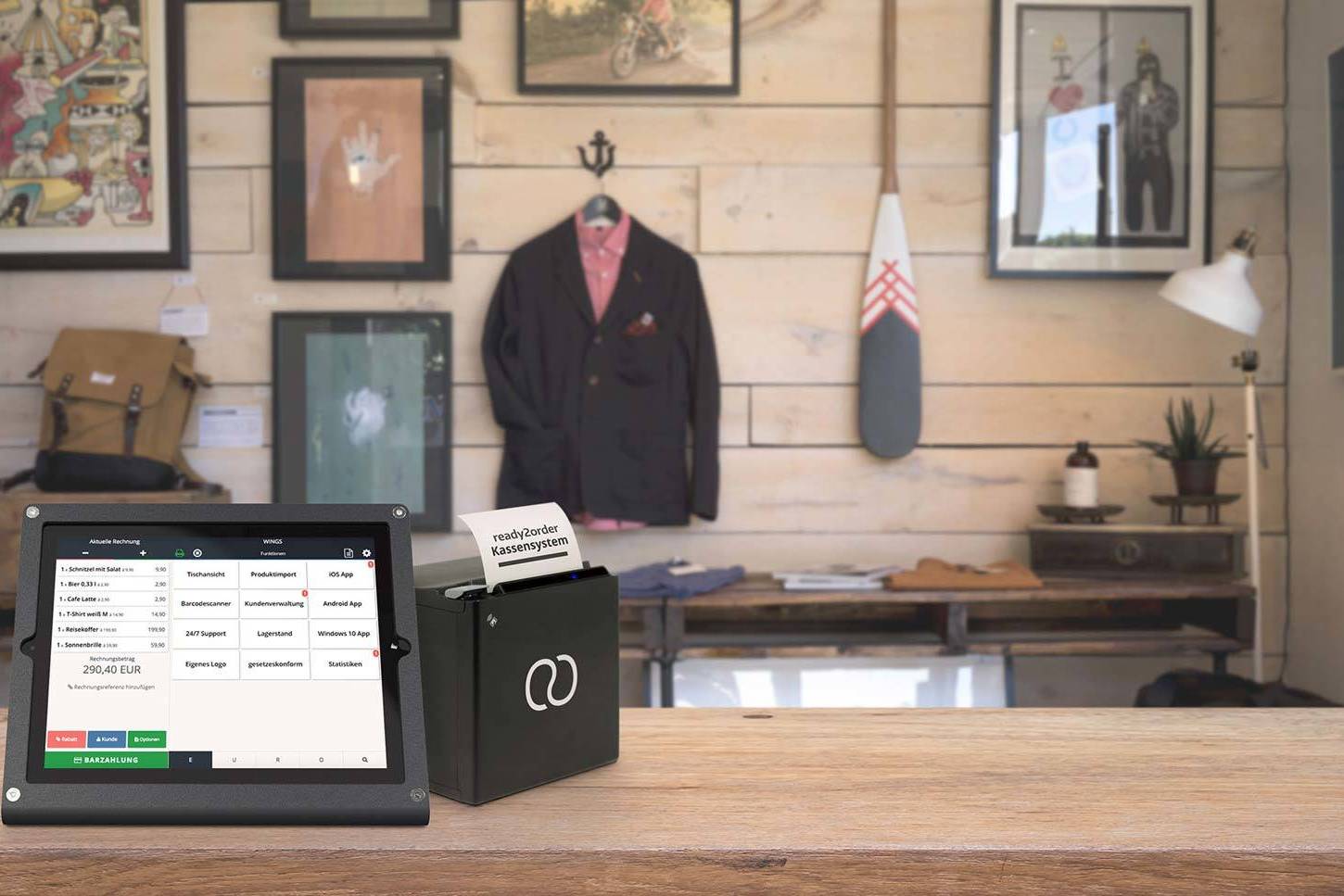
Point of sale systems, warehouse management and branch logistics
A cash register system, also known as a POS system, is software that documents a specific financial…
10. July 2018
Set-up time in production and intralogistics
If a machine or a production site, i.e. individual facilities or entire production lines, is set up…
27. June 2018
The range of storage
The range of storage is a key figure which expresses the internal security of supply by own stocks…
20. June 2018
Cyber-physical systems and logistics
Cyber-physical systems, or CPS for short, are system units or components that are linked together…
24. May 2018
Logistics management and the supply chain
The integrated planning, organization, management, processing and control of the entire flow of…
16. May 2018
Vogel’s approximation method
The approximation method according to Vogel is a heuristic procedure that is mainly used in…
19. April 2018
The screw conveyor / spiral conveyor for bulk material
Transport systems are needed in warehouses to transport goods. For this purpose, there are various…
6. March 2018
Opportunity costs in logistics
Opportunity costs, also known as alternative costs or foregone costs, express a foregone benefit in…
8. January 2018
CPFR – Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment
CPFR stands for Collaborative Planning, Forecasting and Replenishment and is a further development…
5. December 2017
Networked Production: Computer-integrated Manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing, or CIM for short, stands for computer-controlled machine and…
28. November 2017
At a glance: the enterprise resource planning system
An enterprise resource planning system is a software that ensures a smooth flow of commercial…
14. November 2017
The picking time in intralogistics
The picking process itself and the associated picking time are usually a conglomerate of personnel-…
24. October 2017
Picking method Pick-by-robot
The picking type Pick-by-Robot means the picking of goods, carried out by so-called…
16. October 2017
Multicopter: Drones as parcel carriers of the future
Goods delivery by automated or even autonomous drones? What we know at best as a vision from…
10. October 2017
Picking type Pick-by-Scan (also Pick-by-PDT)
The picking method Pick-by-Scan is a paperless picking process that is supported by a portable data…
25. September 2017
Human-machine interfaces in the industry
The human-machine interface represents the analog or digital interaction interface between a…
18. September 2017
Kanban and swarm intelligence at management level
In manufacturing and industry, a supply concept called Kanban(Japanese for card or sign), invented…
12. September 2017
The picking method Pick-by-Vision
Pick-by-Vision is a picking process in which a picker uses data glasses and context-related…
Also available in Deutsch (German)