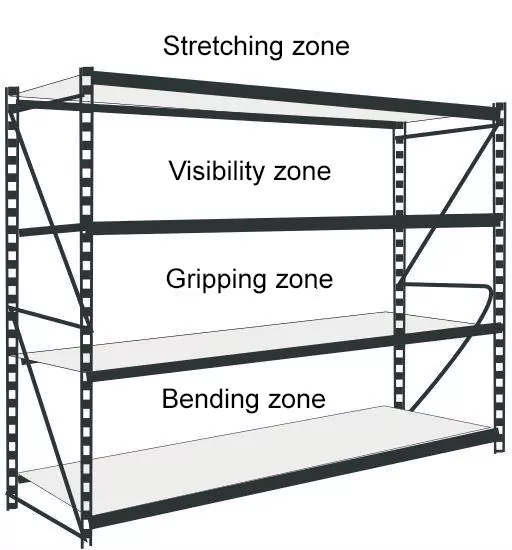
A storage rack, both in intralogistics and retail, can be divided into different horizontal racking zones. This usually results in four racking zones, which are named as follows from bottom to top
- Bending zone
- Gripping zone
- Viewing zone
- Stretch Zone
The height of the shelving zones corresponds essentially to the corresponding designations. The
The height of the shelving zones corresponds essentially to the corresponding designations. Classification is based on the scale of an adult. Accordingly, the material ends up in the
Bending zone on the lowest level, the material in the gripping zone at a relatively suitable gripping height, goods in the viewing zone are at eye level and to remove material from the stretching zone, the material must be gripped on the top level.
Advantages of rack zones
Advantages that result from this division are, for example, a clearer arrangement of goods on the shelf, better ergonomics at the workplace (for example, older employees are only assigned to picking goods in the picking and viewing zone) or a faster due to the structured arrangement and the reduced time required for picking.
Similarly, the different placements allow sales-promoting psychological effects to be exploited at the point of sale, which in turn are used in a targeted manner by manufacturers, brands and store operators. The placements in the respective shelf zones are also subject to different “placement prices”, especially in food retailing, with the visible zone being the most sought-after area.
The individual shelf zones are described in more detail below:
Shelf zones – Bending zone
A shelf can be divided into vertical zones based on the scale of an adult (average height of 1.70 m). The lowest shelf area is called the bending zone. It reaches an average height of 60 – 80 cm.
Goods with low turnover are often stored in the bending zone. However, the expected turnover is not the only decisive factor for the placement of goods. The storage zone close to the floor is also suitable as a storage area for heavy and large-volume goods. In supermarkets, on the other hand, the low-priced products or the low-priced private labels of the respective retail chain are usually found in the back zone.
Bending zone from an ergonomic point of view
For ergonomic reasons, goods with a high turnover volume should not be stored in the bending zone, as the order picker has to make an additional physical effort, for example, if he often kneels down to reach the goods in question. On the one hand, this additional effort is strenuous for the person, on the other hand, it costs additional time during the picking process.
Racking zones – gripping zone
A shelf can be divided into vertical zones based on the scale of an adult (average height of 1.70 m). The grab zone starts at an average height of 60 – 80 cm and reaches accordingly up to a height of 1.40 – 1.60 m.
Employees can reach the gripping zone without any further aids. Therefore, goods that are considered to be handling intensive are usually deposited in this area. Thus, on the one hand, time is saved during order picking due to the fast removal and on the other hand, little energy is consumed by the employees due to the easy removal.
Shelf zones – Visibility zone
A shelf can be divided into vertical zones based on the scale of an adult (average height of 1.70 m). The viewing zone starts at an average height of 1.40 – 1.60 m and reaches up to a height of 1.80 m, depending on the height. The visibility zone is the storage area that ends at the eye level of the order picker. Goods stored in this area are considered to be the most handling intensive.
As with the gripping zone, time and energy are saved by the problem-free removal.
The decisive advantage is that storage and retrieval are the fastest because the order picker can get an overview of the storage area in no time at all. In retail, this also applies to the customer’s view: goods in the visible zone attract the greatest attention from the customer. For manufacturers, this shelf zone is therefore the area in which they prefer to position their brand products.
Shelf zones – Stretch zone
A shelf is divided into vertical zones based on the scale of an adult (average height of 1.70 m). The stretching zone is the uppermost storage area and starts at an average height of 1.80 m.
To store or retrieve goods in the stretching zone requires the most effort. Therefore, goods are often stored in this area which are considered to be the weakest in terms of turnover. During storage and retrieval, the order picker uses various aids such as a ladder, forklift, or storage and retrieval machines for order picking. Using these aids is time-consuming and therefore has a negative effect on picking time.
Conclusion
The division of a shelf into different shelf zones is practiced both in intralogistics in the warehouse and in retail at the point of sale. The placement of a good in each zone depends on its handling intensity, weight, volume and ergonomic factors that affect the work and effort of the order pickers. In retail, on the other hand, the focus of goods placement is more on the customer’s perspective. The aim is to positively influence them and encourage them to buy by placing the products in appropriate shelf zones.
You can find further articles on this topic under Movement Strategies in Warehouse Operations, in particular the single-game strategy. Furthermore, the following articles in the context of retail:
Point of sale and stationary trade – Defnition
Image source: Teaser: © Tiero – Fotolia.com; Image in article – © Rfc1394 License: (CC BY-SA 3.0)
TUP.SML - Mobile data collection with all mobile devices
Optimize your intralogistics processes through the use of customized, multilingual input screens, pick-by-voice, image and text capture, as well as voice control on iOS or Android devices.

Also available in Deutsch (German)